Working Flow Chart of Method Study
Method Study:
Method study is the process of subjecting work to systematic, critical scrutiny to make it more effective and/or more efficient. It is one of the keys to achieving productivity improvement.
It was originally designed for the analysis and improvement of repetitive manual work but it can be used for all types of activity at all levels of an organization. Method study is essentially used for finding better ways of doing work. It is a technique for cost reduction.
The philosophy of method study is that 'there is always a better way of doing a job' and the tools of method study are designed to systematically arrive at this better way of doing a job.
Procedure Involved in Methods Study:
The basic approach to method study consists of the following eight steps. The detailed procedure for conducting the method study is shown in Fig.
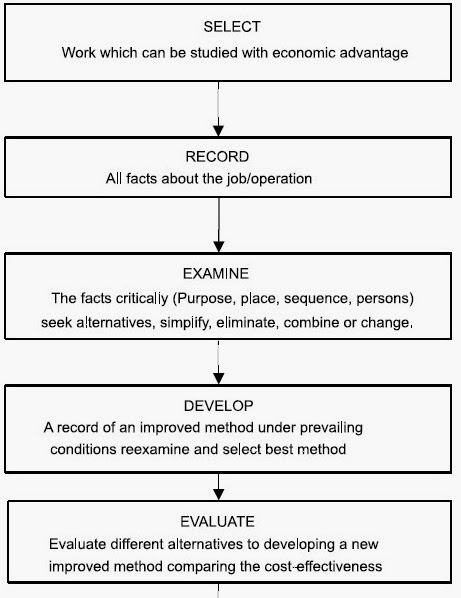
1. SELECT the work to be studied and define its boundaries. The first step, once the Method Study idea is conceived, is the orientation and determination of objectives. The problem must be defined.
2. RECORD the relevant facts about the job by direct observation and collect such additional data as may be needed from appropriate sources. When the job has been selected for Method Study, the next step is to collect and record all the relevant data. The facts collected about the existing method are subsequently subjected to a thorough examination with a view to evolving improved methods. Hence, a clear and precise record is necessary, if method study is to be effective.
3. EXAMINE the way the job is being performed and challenge its purpose, place sequence and method of performance.
4. DEVELOP the most practical, economic and effective method, drawing on the contributions of those concerned.
5. EVALUATE different alternatives to developing a new improved method comparing the cost-effectiveness of the selected new method with the current method with the current method of performance.
6. DEFINE the new method, as a result, in a clear manner and present it to those concerned, i.e., management, supervisors and workers.
7. INSTALL the new method as a standard practice and train the persons involved in applying it.
8. MAINTAIN the new method and introduce control procedures to prevent a drifting back to the previous method of work.
It has been proved that the adoption of such a procedure ensures that no significant point is overlooked and helps in achieving maximum possible results.
The philosophy of method study is that 'there is always a better way of doing a job' and the tools of method study are designed to systematically arrive at this better way of doing a job.
Procedure Involved in Methods Study:
The basic approach to method study consists of the following eight steps. The detailed procedure for conducting the method study is shown in Fig.

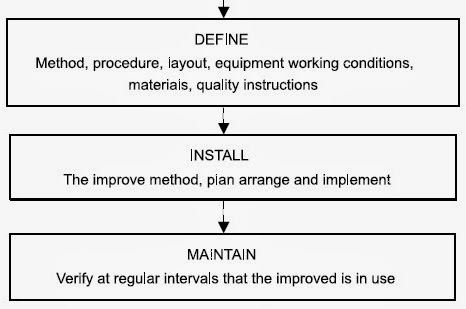 |
| Working flow chart of method study |
2. RECORD the relevant facts about the job by direct observation and collect such additional data as may be needed from appropriate sources. When the job has been selected for Method Study, the next step is to collect and record all the relevant data. The facts collected about the existing method are subsequently subjected to a thorough examination with a view to evolving improved methods. Hence, a clear and precise record is necessary, if method study is to be effective.
3. EXAMINE the way the job is being performed and challenge its purpose, place sequence and method of performance.
4. DEVELOP the most practical, economic and effective method, drawing on the contributions of those concerned.
5. EVALUATE different alternatives to developing a new improved method comparing the cost-effectiveness of the selected new method with the current method with the current method of performance.
6. DEFINE the new method, as a result, in a clear manner and present it to those concerned, i.e., management, supervisors and workers.
7. INSTALL the new method as a standard practice and train the persons involved in applying it.
8. MAINTAIN the new method and introduce control procedures to prevent a drifting back to the previous method of work.
It has been proved that the adoption of such a procedure ensures that no significant point is overlooked and helps in achieving maximum possible results.
Comments
Post a Comment